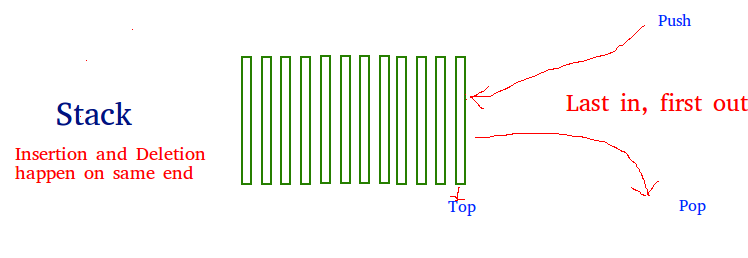
STACK
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed.The order may be LIFO(Last In First Out) or FILO(First In Last Out).
Mainly the following four basic operations are performed in the stack:
-
PUSH
Adds an item in the stack. If the stack is full, then it is said to be an Overflow condition.
-
POP
Removes an item from the stack. The items are popped in the reversed order in which they are pushed. If the stack is empty, then it is said to be an underflow condition.
-
PEEK or TOP
Returns top element of stack.
-
ISEMPTY
Returns true if stack is empty, else false.
How to understand a stack practically ?
There are many real-life examples of a stack. Consider the simple example of plates stacked over one another in a canteen. The plate which is at the top is the first one to be removed, i.e. the plate which has been placed at the bottommost position remains in the stack for the longest period of time. So, it can be simply seen to follow LIFO/FILO order.
Time complexities of operations on stack:
push(),pop(),isEmpty() and peek() all take O(1) time. We do not run any loop in any of these operations.
PROS
The linked list implementation of stack can grow and shrink according to the needs at runtime.
CONS
Requires extra memory due to involvement of pointers.
REFERENCES
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-data-structure-introduction-program/