What is a Matrix?
A matrix is a rectangular arrays of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns.
Matrices are commonly written in box brackets. The horizontal and vertical lines of entries in a matrix are called rows and columns, respectively. The size of a matrix is defined by the number of rows and columns that if contains. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m×n matrix or m-by-n matrix, while m and n are called its dimensions.
The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries.
Provided that they are the same size, Two matrices can be added or subtracted element by element. The rule for matrix multiplication, however, is that two matrices can be multiplied only when the number of columns in the first equals the number of row in the second. Any matrix can be multiplied element-wise by a scalar from its associated field.
Matrices which have a single row are called row vectors, and those which ahve a single column are called column vectors. A matrix which has the same number of rows and columns is called a square matrix. In some contexts, such as computer algebra programs, it is useful to consider a matrix with no rows or no columns, called an empty matrix.

Additionn and Substraction; Scalar Multiplication
Matrix addition, substraction, and scalar multiplication are types of operations that can be applied to modify matrices. These form the basic techniques to work with matrices.
These techniwues can be used in calculating sums, differences and products of information such as sodas that come in three different flavors: apple, orange, and strawberry and two different packaging: bottle and can. Two tables summarizing the total sales between last month and this month are written to illustrate the amounts. Matrix addition, substraction and scalar multiplication can be used to find such things as: the sales of last month and the sales of this month, the average sales for each flavor and packaging of soda in the 2-month period.
Adding and Substracting Matrices
We use matrices to list data or to represent systems. Because the entries are numbers, we can perform operations on matrices. We add or subtract matrices by adding or subtracting corresponding entries.
In order to do this, the entries must correspond. Therefore, addition and subtraction of matrices is only possible when the matrices have the same dimensions. Matrix addition is commutative and is also associative, so the following is true:
A+B = B+A (A+B)+C = A+(B+C)
A-B = B-A (A-B)-C = A-(B-C)
Scalar Multiplication
In an intuitive geometrical context, scalar multiplication of a real Euclidean vector by a positive real number multiplies the magnitude of the vector without changing its direction. What does it mean to multiply a number by 2? It means you add the number to itself 2 times. Multiplying a matrix by 2 means the same thing; you add the matrix to itself 2 times, or simply multiply each element by that constant.
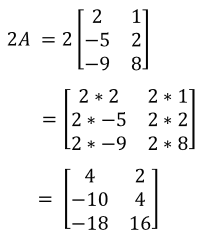
The resulting matrix has the same dimensions as the original. Scalar multiplication has the following properties:
- Left and right distributivity
- Associativity
- Identity
- Null
- Additive inverse
Matrix Multiplication
If A is an n×m matrix and B is an m×p matrix, the result AB of their multiplication is an n×p matrix defined only if the number of columns m in A is equal to the number of rows m in B.Check to make sure that this is true before multiplying the matrices, since there is “no solution” otherwise.
Scalar multiplication is simply multiplying a value through all the elements of a matrix, whereas matrix multiplication is multiplying every element of each row of the first matrix times every element of each column in the second matrix. Scalar multiplication is much more simple than matrix multiplication; however, a pattern does exist.
When multiplying matrices, the elements of the rows in the first matrix are multiplied with corresponding columns in the second matrix. Each entry of the resultant matrix is computed one at a time.

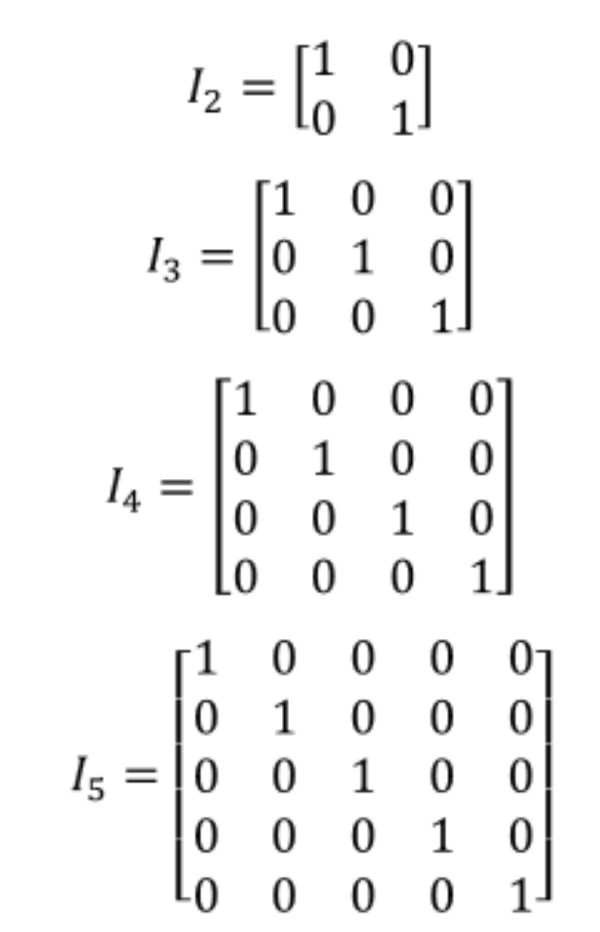
Identity Matrix
The number 1 has a special property: when multiplying any number by 1, the result is the same number, i.e. 5⋅1=5.This idea can be expressed with the following property as an algebraic generalization: 1.x=x.The matrix that has this property is referred to as the identity matrix.
[A][I]=[I][A]=[A]
REFERENCES
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-algebra/chapter/introduction-to-matrices/